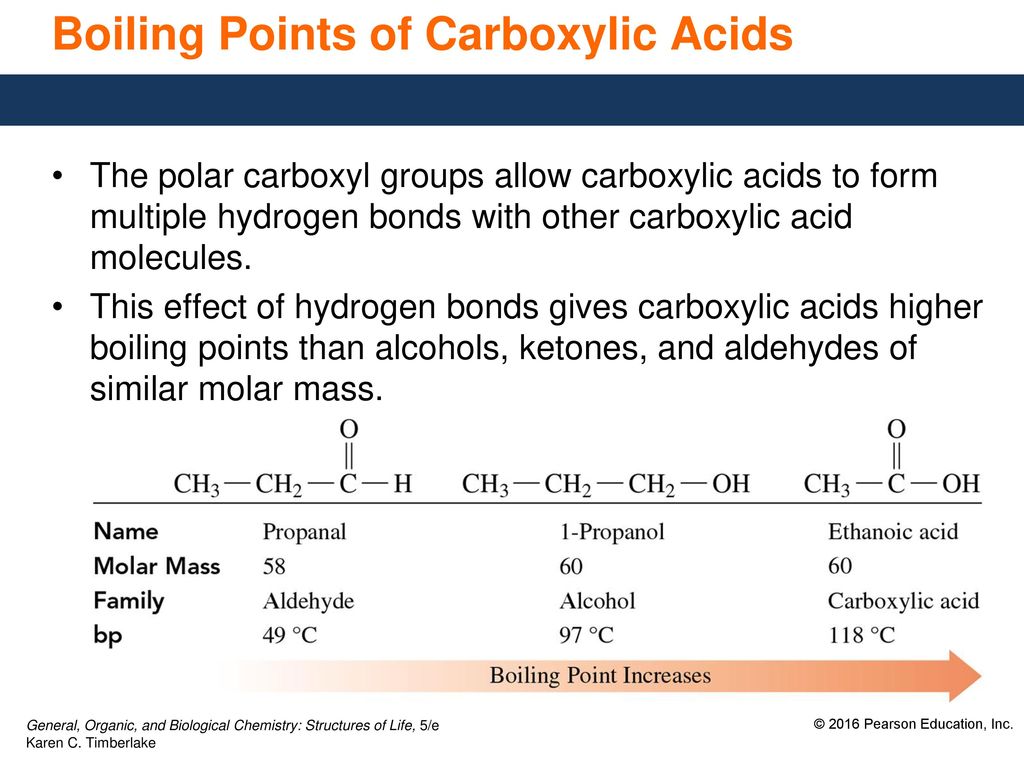
Boiling Point of Ester and Carboxylic Acid
Since 2010 diesel fuel may contain up to 7 vol fatty acid methyl ester FAME in Europe to meet biofuels. Carboxylic acids and carboxylates prevent free water in the gasoline from rusting or corroding.
16 2 Properties Of Carboxylic Acids Ppt Download
They are important in biology being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and.

. The carboxyl COOH group is so-named because of the carbonyl group CO and hydroxyl group. Reaction of alcohol and benzoyl chloride to form ester. How might you account for this trend.
2 is similar in composition to fuel oil no. In ethers the COC angle is 120The moment of inertia about each of the principal axes are I A 3292110 40 gcm 2 I B 3792610 40. Valeric acid or pentanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH 3 CH 2 3 COOHLike other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids it has an unpleasant odorIt is found in the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis from which it gets its nameIts primary use is in the synthesis of its esters.
An ester is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid organic or inorganic in which at least one OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an O alkyl group as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. 63 to 64 C 145 to 147 F. A dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl functional groups COOH.
When bound to avidin HABA exhibits a wavelength absorbance at 500 nm A500 which is proportional to the amount of bound HABA. Application to the Synthesis of α-Functionalized Carboxylic Acids. Because α-amino-ketones self-condense very easily they must be prepared in situThe usual way of doing this is from the relevant oxime via the Neber rearrangement.
Five common classes of these carboxylic acid derivatives are listed in the following table. The mechanism requires zinc and acetic acid as catalysts. Non-toxicUsed to make esters for perfumes and fruit flavors and as an intermediate for food-grade additives.
Functionalization of Alkyl Groups Adjacent to Azoles. Glycolic acid or hydroxyacetic acid. The original Knorr synthesis employed two equivalents of ethyl acetoacetate one of which was.
This prevents the reverse reaction happening. Dimethyl carbonate is often considered. Citric acid can be esterified at one or more of its three carboxylic acid groups to form any of a variety of mono- di- tri- and mixed esters.
It will proceed at room temperature. It is classified as a carbonate esterThis compound has found use as a methylating agent and more recently as a solvent that is exempt from the restrictions placed on most volatile organic compounds VOCs in the US. The following data for isomeric four-carbon alcohols show that there is a decrease in boiling point with increasing substitution of the OH-bearing carbon.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Practice Questions. Although nitriles do not have a carbonyl group they are included here because the functional carbon atoms all have the. Production of esters from carboxylic acid and alcohol.
It is quite different from other acyl chlorides which hydrolyze with formation of hydrogen chloride and the original carboxylic acid. As with carboxylic acids two phosphoric acid molecules may combine with the loss of water to form a di phosphate ester also referred to as pyrophosphate. Arginine is the amino acid with the formula H 2 NHNCNHCH 2 3 CHNH 2CO 2 H.
Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic chemical compound containing one atom each of oxygen and nitrogenIt was likely first synthesized in 1884 but it was not until 5 years later that Siegmund Gabriel correctly assigned the structure. The Four Intermolecular Forces and How They Affect Boiling Points. For comparison in alcohols the COH angle is about 110.
Phenyl oxalate ester is Cyalume the active ingredient in glow sticks. 1-Butanol bp 1175C 2-Butanol bp 935C 2-Methyl-2-propanol bp 322C. For example reaction of ethanoic acid and propanol to form propyl-ethanoate and water.
Glycolic acid is widespread in nature. Has a melting point of -1825 C whereas tetrafluoromethane CF 4. Enolates - Formation Stability and Simple Reactions.
336 to 337 K at 1017 bar Solubility in water. Soluble in most organic solvents and in dilute nitric acid. Boiling point of ethanoic acid is higher than.
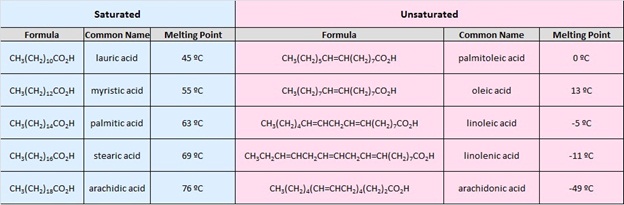
3 Trends That Affect Boiling Points. Decanoic acid is a white crystalline solid with a rancid odor. In general dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acidsDicarboxylic acids are also used in the preparation of.
Salts and esters of valeric acid are known. Concentrated sulfuric acid hydrolysis the formed ethyl ethanoate to. Colorless liquid with a slight characteristic odor and carboxylic acid is a colourless liquid and has a strong odor very much like vinegar.
A glycolate sometimes spelled glycollate is a salt or ester of glycolic acid. The epoxy cycle of ethylene oxide is an almost regular triangle with bond angles of about 60 and a significant angular strain corresponding to the energy of 105 kJmol. 22 Enols and Enolates.
Carboxylic acid any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon C atom is bonded to an oxygen O atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group OH by a single bond. It is used in various skin-care products. B Since the organic compound A with molecular formula MF C8H1602 upon hydrolysis with dil.
The Malonic Ester and Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis. Chemical formula HOCH 2 CO 2 H is a colorless odorless and hygroscopic crystalline solid highly soluble in water. It was named in-line with the HantzschWidman nomenclature and is part of a family of heterocyclic compounds where it.
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOCCO 2 HCH 2 CO 2 H 2. Heat them in the presence of acid catalyst such as sulphuric acid H 2 SO 4 is used as a catalyst. The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as HO 2 CRCO 2 H where R can be aliphatic or aromatic.
A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen H atom or to some other univalent combining group. At physiological pH the carboxylic acid is deprotonated CO 2 and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated resulting in a cationOnly the l-arginine symbol Arg or R enantiomer is. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol.
Ethanol reacts with acetic acid to give ethyl ethanoate which is an ester compound. It works well because the ester has the lowest boiling point of anything present. Dimethyl carbonate DMC is an organic compound with the formula OCOCH 3 2It is a colourless flammable liquid.
H2S04 gives carboxylic acid B and the alcohol C therefore it must be an ester. Carboxylic acid and alcohol. CH 3 CO 2 H.
Hydrolysis of ester gives carboxylic acid and. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. 16 C 3 F.
The boiling range is generally 160360C 320680F. To make a small ester like ethyl ethanoate you can gently heat a mixture of ethanoic acid and ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid and distil off the ester as soon as it is formed. Further since oxidation of C with chromic acid produces the acid B therefore both the carboxylic acid B and the alcohol C must contain the same number.
The most common method to measure the degree of biotinylation of a sample is using 4-hydroxyazobenzene-2-carboxylic acid HABA dye which noncovalently binds to avidin in the absence of biotin. 257 K Boiling point. However as phosphoric acid has further -OH functionalities triphosphates may also be formed.
The melting and boiling points of chloro- bromo- and iodoalkanes are higher than the analogous alkanes scaling with the atomic weight and number of halides.
21 1 Structure And Properties Of Carboxylic Acids And Their Salts Chemistry Libretexts

Physical Properties Of Carboxylic Acids Youtube

Carboxylic Acid Have Higher Boiling Points Than Aldehydes Ketones And Even Alcohol Of Youtube


Comments
Post a Comment